Aluminium casting knowledge
Discover the fundamentals of Aluminium Casting knowledge! Learn about reactions of melt with its environment, oxide skin formation, entrainment processes and surface turbulence.
In the book “Complete Casting Handbook”
Metal Casting Processes, Metallurgy, Techniques and Design
by John Campbell
Selected Contents
Casting Metallurgy
The Melt
- Reactions of Melt with its Environment
- Transport of Gases in Melt
- Surface Film Formation
- Vaporisation
Entrainment
- Entrainment Defects
- Bifilms
- Bubbles
- Extrinsic Inclusions
- Entrainment Processes
- Surface Turbulence
- Oxide Skins from Melt Charge Material
- Pouring
- Oxide Lap Defect I: Surface Flooding
- Oxide Lap Defect II: The Confluence Weld
- The Oxide Flow Tube
- Microjetting
- Bubbles Trails
- Furling and Unfurling
- Deactivation of Entrained Films
- Soluble, Transient Films
- Detrainment
- Evidence for Bifilms
- The Importance of Bifilms
- The Four Common Populations of Bifilms
Flow
- Effect of Surface Films on Filling
- Effective Surface Tension
- The Rolling Way
- The Unzipping Way
- Fluidity
- Fluidity Definition
- Mode of Solidification
- Effect of Velocity
- Effect of Viscosity
- Effect of Solidification Time
- Effect of Surface Tension
- Effect of an Unstable Substrate
- Comparison of Fluidity Tests
- Effect of Vibration
- Extended Fluidity
- Continuous Fluidity
Moulds and Cores
- Moulds: Inert or Reactive
- Transformation Zones
- Evaporation and Condensation Zones
- Mould Atmosphere
- Mould Surface Reactons
- Metal Surface Reactions
- Mould Coatings
Solidification Structure
- Heat Transfer
- Development of Matrix Structure
- Segregation
Casting Alloys
- Zinc Alloys
- Aluminium
- Oxide Films on Al Alloys
- Entrained Inclusions
- Grain Refinement (Nucleation and Growth of the Solid)
- Dendrite Arm Spacing (DAS) and Grain Size
- Modification of Eutectic Si in Al-Si Alloys
- Iron-Rich Intermetallics
- Other Intermetallics
- Thermal Analysis of Al Alloys
- Hydrogen in Al Alloys
- Copper Alloys
- Cast Iron
- Steels
- Nickel-Base Alloys
- Titaniun
Porosity
- Shrinkage Porosity
- Gas Porosity
- Porosity Diagnosis
Cracks and Tears
- Hot Tearing
- Cold Cracking
Properties of Castings
- Test Bars
- The Statistics of Failure
- Effects of Defects
- Tensile Properties
- Fracture Toughness
- Fatigue
- Elastic (Young’s) Modulus and Damping Capacity
- Residual Stress
- High Temperature Tensile Properties
- Oxidation and Corrosion Resistance
- Leak Tightness
- Surface Finish
- Quality Indices
- Bifilm-Free Properties
Casting Manufacture
- Introduction to the Casting Manufacture
Section 1
The 10 Rules for Good Castings
- Rule 1: Use a Good-Quality Melt
- Rule 2: Avoid Turbulent Entrainment (The Critical Velocity Requirement0
- Rule 3: Avoid Laminar Entrainment of the Surface Film (The Non-Stopping, Non-Reversing Condition)
- Rule 4: Avoid Bubble Damage
- Rule 5: Avoid Core Blows
- Rule 6: Avoid Shrinkage Damage
- Rule 7: Avoid Convection Damage
- Rule 8: Reduce Segregation Damage
- Rule 9: Reduce Residual Stress
- Rule 10: Provide Location Points
Section 2 – Filling System Design
Fundamentals
- The Maximum Velocity Requirement
- Gravity Pouring^ The “No-Fall” Conflict
- Reduction or Elimination of Gravity Problems
- Surface Tension Controlled Filling
Components
- Pouring Basin
- Sprue (Down-Runner)
- Runner
- Gates
- Surge Control System
- Vortex System
- Inclusions Control: Filter and Traps
- Filter
Design Practice
- Background to the Methoding Approach
- Selection of a Layout
- Weight and Volume Estimates
- Pressurised Versus Unpressurised
- Selection of a Pouring Time
- Thin Sections and Slow Filling
- Fill Rate
- Pouring Basin Design
- Sprue (Down-Runner) Design
- Runner Design
- Gate Design
Section 3 – Processing (Melting, Moulding, Casting, Solidifying)
Melting
- Batch melting
- Liquid Metal Delivery
- Reverberatory Furnaces
- Crucible Melting (Electric Resistance or Gas Heated)
- Induction Melting
- Automatic Bottom Pouring
- Continuous Melting
- Tower (Shaft) Furnaces
- Dry Hearth Furnaces for Non-Ferrous Metals
- Holding, Transfer and Distribution
- Holder Failure Modes
- Transfer and Distribution Systems
- Melt Treatment
- Degassing
- Detrainment (Cleaning)
- Additions
- Pouring
- Cast Material
- Re-Melting Processes
Moulding
- Inert Moulds and Cores
- Aggregate Moulding Materials
- Binders
- Other Aggregate Mould Processes
- Rubber Moulds
- Reclamation and Re-Cycling Sands
Casting
- Gravity Casting
- Horizontal Transfer Casting
- Counter-Gravity
- Centrifugal Casting
- Pressure-Assisted Casting
- Lost Wax and Other Ceramic Mould Casting Processes
- Lost Foam Casting
- Vacuum Molding (V Process)
- Vacuum-Assisted Casting
- Vacuum Melting and Casting
Controlled Solidification Techniques
- Conventional Shaped Casting
- Directional Solidification
- Single Crystal Solidification
- Rapid Solidification Casting
Dimensional Accuracy
- The Concept of Net Shape
- Mould Design
- Mould Accuracy
- Tooling Accuracy
- Casting Accuracy
- Metrology
Post-Casting Processing
- Surface Cleaning
- Heat Treatment
- Hot Isostatic Pressing
- Machining
- Painting
- Plastic Working (Forging, Rolling, Extrusion)
- Impregnation
- Non-Destructive Testing
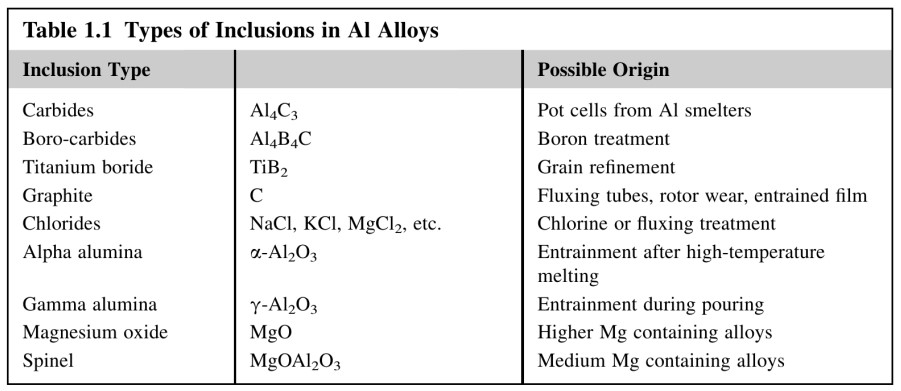
Several pictures from this book that refer to aluminium
To Table 1.1 – Nearly all of these foreign materials will be deleterous
to products intended for such products as foil or computer discs.
However, for shaped casting, those inclusions such as carbides and borides
may not be harmful at all. This is because having precipitated from melt,
so they are usually therefore in excellent atomic contact with matrix.
 Figure 2.1 – Sketch of a surface entrainment event
Figure 2.1 – Sketch of a surface entrainment event
 Figure 2.4 – Entrainment defects:
Figure 2.4 – Entrainment defects:
(a) a new bifilm; (b) bubles entrained as an integral part of the bifilm;
(c) liquid fluxtrapped in a bifilm; (d) surface debris entrained with the bifilm;
(e) sand inclusions entrained in the bifilm;
(f) an entrained surface film contained integral debris