Explosive Welding of Aluminium
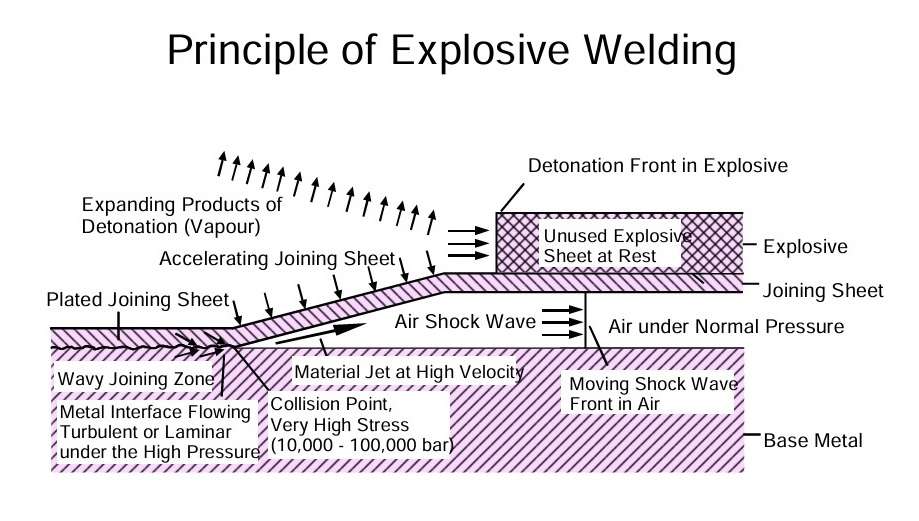
Principle of Explosive Welding
Shock waves (3,000 to 9,000 m/s) can produce pressures of up to 6 x 106 N/cm2. This energy is utilised for explosive welding, especially for plates with large areas. The shock waves spread out and create a “material wave” at the joining plane. At the collision point a thin jet of material is heated to a high temperature, causing melting and mechanical mixing at the interface. Aluminium can be effectively welded with itself and also with steel and copper giving composite joints.
Figure 1 – Principle of explosive welding
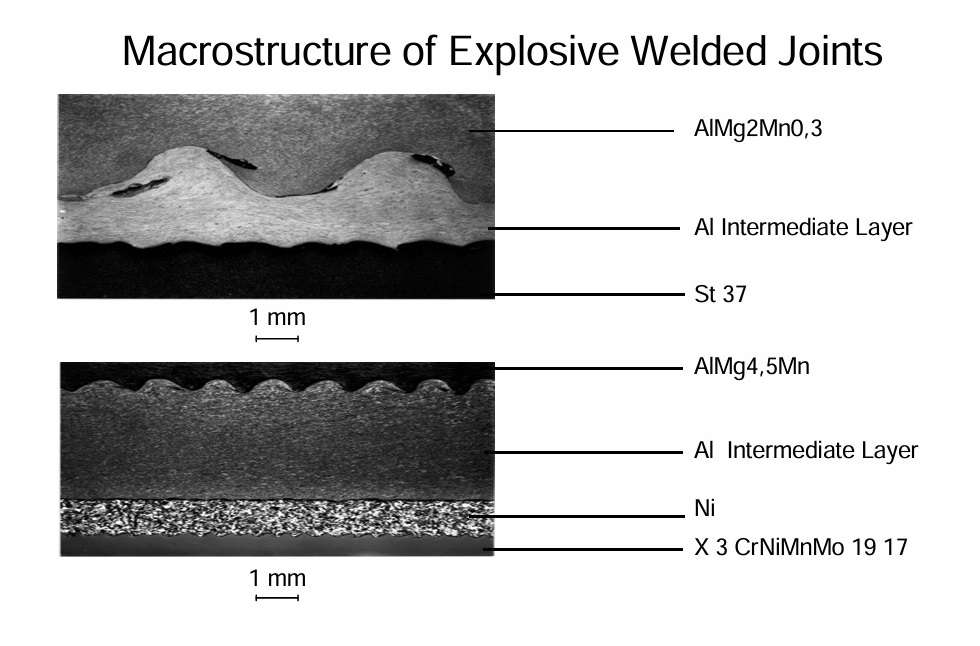
Macrostructure of Explosive Welded Joints
The detonation force waves can be clearly seen as waves in a microsection. “Multiple explosive welding” can be used to join a number of materials of different thicknesses. Even here it is possible to join materials which cannot be joined by other processes.
Figure 2 – Macrostructure of explosive welded joints
The source:
TALAT Lecture 4300 – Beam Welding Processes of Aluminium / Ulrich Krüger – European Aluminium Association, 1994