The factors of anodised aluminium streaking
Learn about the causes and solutions for anodised aluminium streaking defects in extrusions. Understand how the gloss of the anodized surface is affected by the roughness of the original surface.
The origin of anodised aluminium streaking
Streaking anodising defects is often present on anodized extrusions of AlMgSi aluminium alloys (Figure 1). The cause of these defects is a difference in intensity and diffuse nature of the reflected light. An anodic coating is formed on the top of the aluminium surface. The gloss of the final anodized surface depends mainly from the roughness of this original surface (Figure 2).
 Figure 1 – The example of streaking anodising defects [1]
Figure 1 – The example of streaking anodising defects [1]
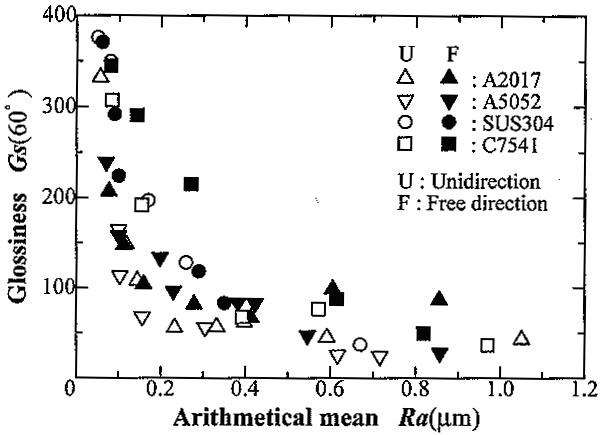 Figure 2 – Relationship between roughness and glossiness
Figure 2 – Relationship between roughness and glossiness
of various materials, including aluminum alloys (Yonehara et al) [1]
Alkaline etching
Alkaline etching is the common pre-treatment stage for anodized aluminium extrusions.
The aim of alkaline etching is to produce a uniform matt surface. However, the etching process can generate surface imperfections due to uneven chemical attack of the various surface microstructure of aluminium extrusions (Figure 3).
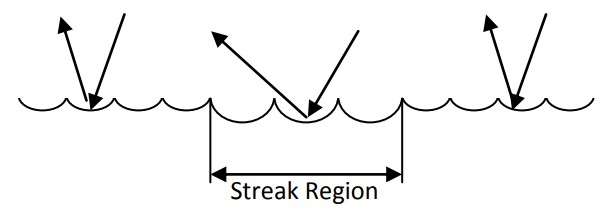 Figure 3 – Reflectance of light is altered in and out of the streak zone
Figure 3 – Reflectance of light is altered in and out of the streak zone
due to differences in etching pit size and number [2]
Some extrusion surface defects such as pick-up and die lines may not be removed completely from the etched surface. Their traces are a part of the surface imperfections on the etched surface.
The microstructure of anodised aluminium streaking
Microstructure imperfections
The most common surface imperfections are created on the extrusion surfaces during alkaline etching are:
- etching pits
- grain boundary grooves
- grain etching steps
- surface-defect-traces
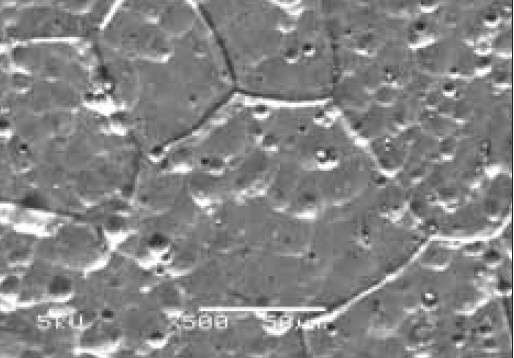 Figure 4 – Alkaline etching pits [3]
Figure 4 – Alkaline etching pits [3]
 Figure 5 – Deep grain boundary grooves [3]
Figure 5 – Deep grain boundary grooves [3]
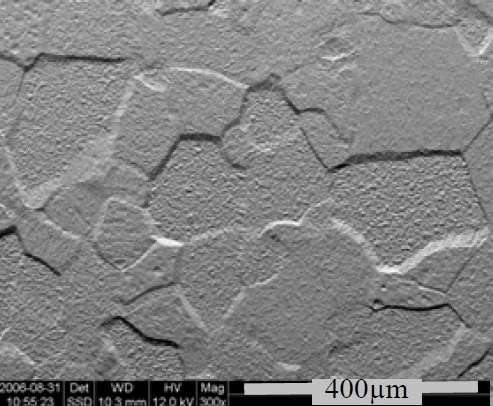 Figure 6 – Grain etching steps [5]
Figure 6 – Grain etching steps [5]
 Figure 7 – Die-line traces on the etched aluminium extrusion [3]
Figure 7 – Die-line traces on the etched aluminium extrusion [3]
Etching pits
Etching pits are created due to different reaction rates between intermetallic particles or inclusions and the aluminium matrix.
In 6xxx series aluminium alloys, the major intermetallic phases are:
- primary Fe-rich intermetallic particles and
- Mg2Si precipitates.
During etching, the detachment of the Fe-rich intermetallic particles from the Al matrix results in the formation of large etching pits with size up to 10 μm on the etched surface [2, 4].
The detachments of inclusions or contaminants produce very large etching pits with irregular shape corresponding to the size and shape of the inclusions or contaminants.
The preferential dissolution of Mg2Si precipitates leads to the formation of small etching pits with size directly related to the original size of the precipitates.
Grain boundary grooves
Grain boundary grooves are formed due to preferred grain boundary attack during etching. The severity of grain boundary grooves depends on whether grain boundaries are attacked in preference to the matrix and on the kinetics of the attack [2].
Grain etching steps
Grain etching steps are created on the surface of polycrystalline materials due to pronounced chemical attack of particular crystal planes [2,3]. After etching, the surfaces of pronouncedly at tacked planes are lower than for other planes, forming grain etching steps [2, 3].
Surface-defect-traces
Surface-defect-traces may be present on the etched surface due to insufficient etching or serious extrusion surface defects etc. [2, 8].
Overall, surface imperfections are created on the extrusion surface due to uneven chemical attack on the surface microstructure during etching. Consequently, the intensity of streak defects depends on the surface microstructure as well as its degree of homogeneity, which are influenced by various factors involved in the different processing steps of the anodized extrusions [8].
The factors of anodised aluminium streaking
The influence of various manufacture process variables on the formation of streak defects includes:
- Billet quality
- chemical composition
- iron
- copper
- zinc
- macro- and microstructure
- surface inverse segregation
- surface chill zone
- contaminants
- billet skin
- oxide shell
- inclusions
- lubricants
- Extrusion process
- extrusion parameters
- container temperarure
- billet temperature
- extrusion speed
- extrusion temperarature
- butt thickness
- extrusion equipment
- bearings length
- bearing maintenance
- press alignment
- die design
- the position of ports
- weld chambers
- Etching
- etching solution composition
- alkaline
- aluminium
- additions
- solution temperature
- etching time
- etching solution composition
- extrusion parameters
- chemical composition
Sources:
- Mechanisms of Streaking on Anodized 6xxx Series Extrusions / X. Zhang, H. Zhu, A.K. Dahle, M.J. Couper – ET Seminar, Chicago, 2008.
- Streaking on Aluminium anodized extrusions / J. Walker – Master of Engineering Thesis, AUT University, 2012
- Etching effects and formation of Streaking Defects on Al Extrusions / H. Zhu, M.J. Couper, A.K. Dahle – Aluminium International Today, May/June 2011.
- Effect of Process Variables on the Formation of Streak Defects on Anodized Aluminum Extrusions: An Overview / Y. Zhu, M.J. Couper, A.K. Dahle – High Temp. Mater. Proc., Vol. 31 (2012), pp. 105-111.
- Aspects of Preferential Grain Etching During Alkaline Pre-Etching Step Before Anodizing of Aluminum Profiles / Ø. Bauger, H. Bjerkaas – ET Seminar, 2012.